How To Find Displacement On A Position Time Graph
In this article, we will learn how to notice displacement on a position-fourth dimension graph. Aposition-time graph is a graph where the instantaneous position \(x\) of a particle is plotted on the y-axis and the time \(t\) on the 10-axis. The position-time graph shows you where an object is located over a certain interval of time or at any detail instant of time.
Displacement of whatsoever object is defined as the alter in position of the object in a fixed direction. Information technology is given past the vector fatigued from the initial position to the last position of the object.
Displacement is a vector quantity i.e., information technology has both magnitude and direction. Displacement of an object can exist positive, negative and zero.
How to observe displacement on a position-time graph
To learn how you tin can find displacement on a position-time graph consider the figure given beneath that shows a position-time graph of any object.
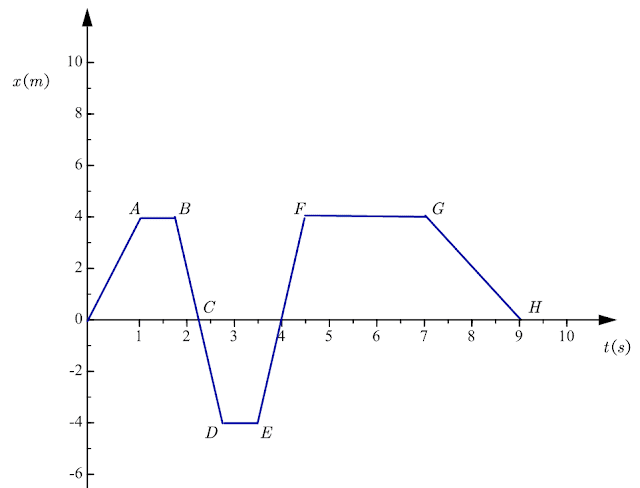
Now from the above figure, nosotros can see that our object under consideration starts its journey from the origin at initial time \(t=0\) and position \(10=0\). Information technology reaches its final position at the time \(t=9s\) represented by point \(H\) on the position-time graph.
Let us at present find the deportation of the object when it reaches point \(A\) marked on the graph. Let the states now draw a line to get a projection of indicate \(A\) on the y-centrality to go the position of the object when it reaches point \(A\). The figure given below shows the project of various points on both the x-axis and the y-centrality.
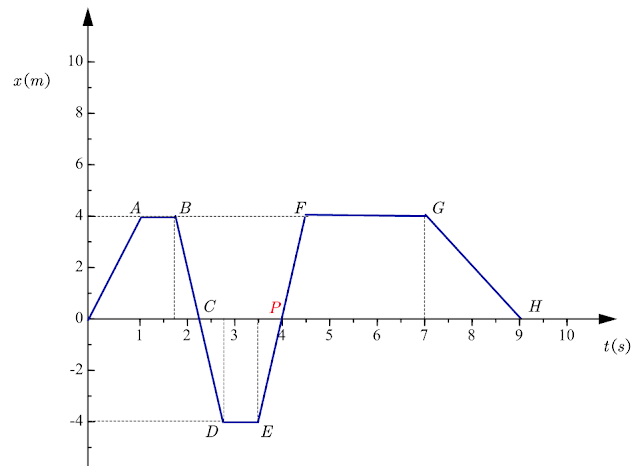
The project of a betoken \(A\) on the y-axis is at the indicate \(4m\) from the origin. So,
Position of the object with respect to the origin when it reached point \(A\) \(= 4m\)
Position of the object with respect to the origin when information technology reaches point \(B\) \(= 4m\)
From the position-time graph, we tin encounter that the projection of \(B\) on the y-axis is at position \(ten=4m\) which means the object is at rest and has non moved with the passage of time.
Similarly, you tin can detect the position of the object at diverse points with respect to the origin \(O\) or initial position of the object.
Let us at present find the deportation of the object between time \(t=0\,\,s\) to \(t=3.5\,\,s\).
At \(t=4s\) our object is at point \(P\).
We know that displacement is a change in the position of the object.
Here,
\(x_0=0m\)
\(x_{three.5}=-4m\)
So, modify in position = displacement =\(x_{3.five} – x_0\,\,=\,\,-4-0=-4m\)
Notation that here deportation is negative. Negative deportation means distance in the negative direction. And then, instead of four thou forward from the origin, the object is 4 m astern from the origin.
Let us now find the displacement of the object between time \(t=0\,\,s\) to \(t=4\,\,s\).
At \(t=4s\) our object is at bespeak \(P\).
Here
\(x_0=0m\)
\(x_4=0m\)
And so, change in position = displacement =\(x_4 – x_0\,\,=\,\,0m\)
Similarly, y'all tin detect deportation between any time interval using the position-fourth dimension graph.
Related Articles
- How to detect displacement on velocity-time graph
- How to detect boilerplate velocity on a position-fourth dimension graph
- How to discover instantaneous velocity on a position-time graph
Source: https://www.physicsgoeasy.com/how-to-find-displacement-on-a-position-time-graph/
Posted by: thomsensoffeas.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Displacement On A Position Time Graph"
Post a Comment